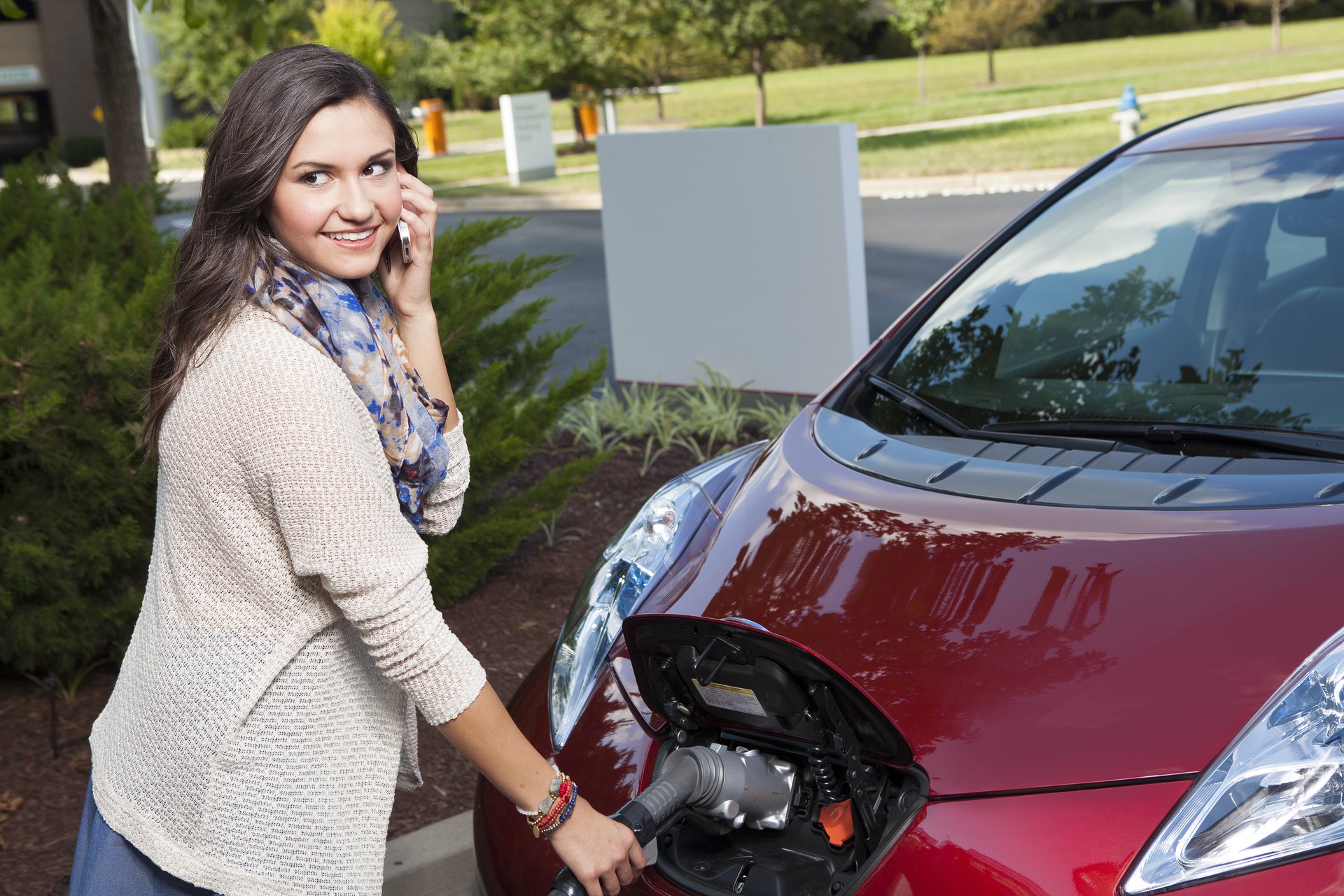
EVs (electric vehicles) are becoming more popular for many obvious reasons. You can no longer deny the impacts of climate change on the world. Governments and individuals alike are increasing their focus on minimizing fossil fuel emissions.
While the upfront costs of electric cars are higher, it can be affordable to run an EV because of the reduced cost of electricity compared to diesel and petrol.
With the government electric car charger grant (EHSS), private residential buildings can receive up to HKD 15 million to install EV charging-enabling infrastructure, which allows EV owners to install chargers at their car parks of their residences in the future in an easy manner.
How EV Charging Works
Similar to any car, electric vehicles require refueling. For this advanced car, all you should do is plug the vehicle into a source of electricity and consider leaving it for some time.
It is also like charging a mobile phone in that every kind of model will need a different type of cable so as to make the connection.
Basically, there is a port on your EV and another port on your charging station. Your charger should plug in both ports.
Types of EV Chargers
According to experts at Cornerstone Technologies Limited, EV (electric vehicle) charging points are of three major types. These include rapid, fast, and slow.
Rapid Chargers
They are the fastest way to charge your electric vehicle. You might have seen these at locations or motorway services near the main routes.
Electric cars can get recharged at 80% capacity within 20 minutes based on the kind of model. This explains why they are referred to as rapid chargers. On average, an electric car will take about one hour to charge fully on a standard rapid charge point of 50kW.
Fast Chargers
These have a power output ranging from 7kW to 20kW. They are twice faster than slow chargers. Most home wallbox chargers, which you may buy, have this type of power output, with around 11kW available in every British house. But this depends on the supply you have at home, not the wallbox you invest in.
An 8kW connection can charge your Nissan Leaf within five hours, whereas a 20kW connection can charge the same in two hours or less. You can as well install a fast-charge wallbox charger at home, as long as the electrics in the house are up to it.
Slow Chargers
Mostly, these chargers are rated up to around 3kW. It will take you about 10 hours to fully charge your car.
Although it is possible to carry out slow charging using 3-pin sockets, you should consider installing a dedicated charger at home, especially if you will be charging your car regularly.
Charging Solutions
There are two major kinds of charging solutions you can have at home. These two charging solutions are discussed below:
- Level 2: EV chargers are separately sold from the vehicle, even though they are normally bought at the same time. These chargers need a little bit complicated setups, as you will need to plug them into the 240V outlet that allows charging five times faster based on the charger and electric vehicle you have. All these chargers have SAE J1772 connectors, plus you can buy them online in the US and Canada. For all plug-in hybrid or electric cars, the use of a level 2 home charging solution is advisable to enable you to enjoy your vehicle’s full potential and charge it faster.
- Level 1: Charging usually happens when you charge your EV using a charger inside your vehicle. These chargers might be plugged with, one end in the standard 120V outlet and the other end getting plugged into your car directly. It may charge 124 miles or 200 kilometers within 20 hours.
Charging Speed and Tech
At its core, batteries in electric vehicles are similar to supersized versions of batteries in a mobile phone. These batteries hold DC (direct current) electricity and deliver this power on demand.
Similar to smartphones, charging electric vehicles is simple. You will just need to plug it in. However, the battery’s size means it will need more electricity and more time off to fully recharge.
How faster your car recharges depends on how much electricity will be drawn, the battery’s size, and how much electricity your vehicle can accept.
Where to Charge Electric Vehicles
Looking for a place to recharge your car can be simple. With a lot of convenient options out there, you can charge your car at work, at a public charging station, and at home.
Charging your EV at work is becoming an added advantage that benefits every electric car owner. It will allow you corporate sustainability efforts and promote cleaner transportation.
As mentioned, you can charge your car home with level 2 and level 1 chargers. Charging your EV at home takes care of your charging requirements, but it would be best to be familiar with public charging.
Normally, public charging is at level 3 and level 2, and its costs differ. Using a Charging Network Map, you may easily explore hundreds of stations in the country. Most charging stations are managed privately, whereas others are either utility-owned or state-owned facilities.
In order to use a public charging station, you will need to first register with one of the utilities or operating companies. You can use them with a smartphone app, a charge card, or a membership code/number.
Final Remarks!
Electric cars are not just a way to travel from one point to another. They are also a revolution. They run on electricity, either in part or completely, and mark the beginning of changing from fuel-powered cars to greener or cleaner ways of driving. Regardless of their slow approval in some countries, these electric cars are here to stay.